Disclosure of information in line
with the TCFD Recommendations
In June 2022, SBI ARUHI announced its support for recommendations published in June 2017 by the Task Force of Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB).
In line with the TCFD recommendations, the company identified risks and opportunities presented by climate change, analyzed and assessed the financial implications, and considered actions with focus on resilience. This page contains detailed information on this subject.
SBI ARUHI will continue to assess and manage climate-related risks and opportunities, disclose information adequately, enhance the resilience of actions to tackle climate change, and play its role as a financial institution to drive transition to a carbon-free economy.

Governance
SBI ARUHI has established an ESG Committee chaired by CEO and consisting of the same members as the Executive Committee members. The ESG Committee considers and implements actions to address climate-related challenges as a part of environmental initiatives.
The ESG Committee meets quarterly as a general rule to discuss the mid- and long-term sustainability trends of the company and the society and develop/implement specific initiatives and actions to address climate change and other ESG challenges. The committee also submits half-yearly reports to the Board of Directors about progress in the initiatives and actions.
The Board of Directors supervises matters reported by the ESG Committee from the standpoint of improving corporate value, and determines ESG policies, Materiality, and key performance objectives for addressing climate change and other issues based on the results of discussions at the ESG Committee.
SBI ARUHI has also established the ESG Task Force presided by CFO under the ESG Committee. The task force is responsible for driving and supporting the implementation of actual initiatives and actions against climate change and ESG challenges as determined by the ESG Committee.
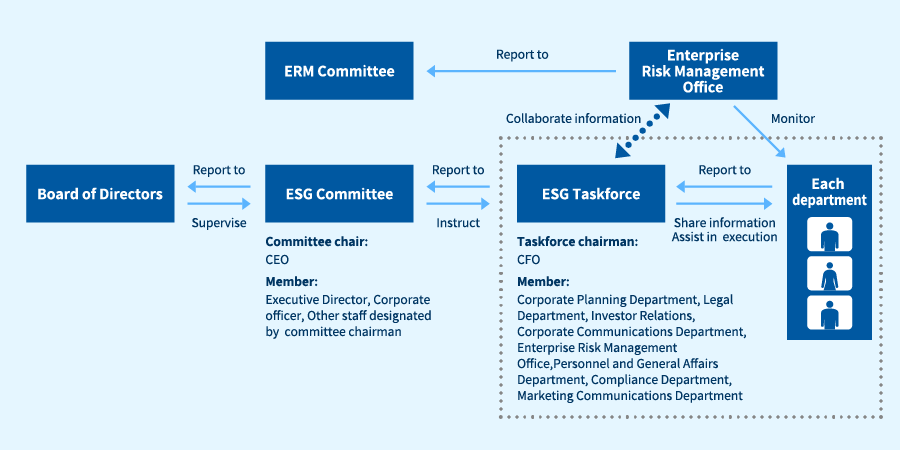
*SBI ARUHI positions climate-related actions as a part of its environmental initiatives and
clearly defines that they should be handled by the ESG Committee.
Strategy
SBI ARUHI's housing loan business is so called mortgage banking involving origination (lending) and servicing (collection) of housing loans funded by means of securitization mainly as a money lender under the Money Lending Business Act in Japan.
Specifically, SBI ARUHI transfers its regidential mortgage to the Japan Housing Finance Agency (JHF), trust banks, and other financial institutions. Then, residential mortgage-backed securities collateralized by these housing loan receivables or trust beneficiary rights are issued and sold to investors. This minimizes the funding risk, interest rate risk, credit risk, and other risks associated with business operations. The Company is also commissioned by the JHF, trust banks, and other financial institutions to manage and collect receivables even after the transfer of housing loan receivables. In addition, The Company is a bank agency as defined in the Banking Act in Japan to sell housing loan products of partner financial institutions and other organizations.
Housing loan receivables originated by SBI ARUHI group are normally transferred. At the same time, housing loan products sold by the group on behalf of other financial institutions are not reflected in its balance sheet. Therefore, the group's mortgage business is characterized by fee business with minimal credit risks and interest rate risks. SBI ARUHI also issued the first Green RMBS (*1) in Japan, procuring funding for the execution of “ARUHI Super Flat S” (*2) housing loans for residential properties that satisfy certain standards on energy saving.
Because of this business model, SBI ARUHI has not seen associated risks in scenario analysis, such as decreased collectivity due to damage to mortgaged properties, which could pose significant risks for owning housing loan receivables. Rather, The Company sees great business opportunities in the growing momentum for sustainable investment in recent years.
To environmental initiatives, SBI ARUHI operates its business based on the commitment to "to contribute to the creation of a stock-based circular society in which people pass on and extendedly use good products" and "to promote the spread of environmentally friendly housing."
Based on the idea described above, SBI ARUHI addresses environmental issues including climate change as a part of its critical management challenges. By helping broad adoption of energy-efficient houses, The Company contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- *1 RMBS is an abbreviation of Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities. Refers to securities issued with the collateral of housing loan receivables. Green RMBS refer to those issued with housing loans for acquiring residential property expected to have a high environmental improvement effect as the underlying assets.
- *2 “ARUHI Super Flat S” is an original SBI ARUHI product using the housing loan insurance (guarantee type) system in which “ the JHF paying an insurance claim to a private-sector financial institution when a customer is unable to repay a housing loan provided by a private-sector financial institution.” It refers to housing loans that use the “Flat 35”S system for lowering the initial interest rate for a fixed period for properties that meet the criteria specified by the Japan Housing Finance Agency.
Identifying and assessing climate-related risks and opportunities
For identifying and assessing risks and opportunities presented by climate change, SBI ARUHI examined possible situations in 2050 in two scenarios along with TCFD recommendations: (1) Maintaining global warming below 1.5℃ under a sustainable development model (using 1.5℃ scenario, IPCC SSP1-1.9 scenario as reference), and (2) Maximum emissions without climate-related policies in place under a fossil-fuel-reliant development model (using 4℃ scenario, IPCC SSP5-8.5 scenario as reference).
SBI ARUHI has also conducted a qualitative analysis of climate-related risks (transition risks, physical risks) and opportunities in the short term (5 years), medium term (10 years), and long term (30 years).
Climate-related risks and key initiatives
Risks and key initiatives in scenario analysis
| Category | Major risks | Time frame | Financial impact | Key initiatives | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transition risks |
Policy & legal | “Flat 35” program may be revised as the government promotes energy saving policies. If energy saving technology criteria are tightened, more new houses become ineligible for Flat 35, leading to drop in “ARUHI Flat 35" origination and decrease in operating revenue. | Medium- to long-term | Big |
- Support people to move to pre-owned houses and green their homes to increase opportunities to offer housing loans supporting maintainability, manageability, and energy saving performance of houses and drive profitability.
- Consider urging the government to implement a policy to promote energy saving initiatives across the housing loan industry. - Consider conducting industry-wide activities to urge implementation of the policy. |
| Technology | Adoption of more energy saving buildings, lighting, air conditioning, and servers at head office and sales branches would increase SG&A (initial costs) in the short term. | Short-term | Small | - This will lead to lower SG&A (running cost) in the medium and long term. SBI ARUHI will control cost adequately and make capital investments from the medium- and long-term viewpoint. | |
| Policy & legal/ Technology/ Market |
Housing prices will increase along with soaring cost of building materials (including interior, house equipment, etc.) with tightening of regulations on carbon tax, timber, plastic, and energy saving housing and implementation of ZEH requirements. This will discourage consumers to purchase houses, leading to smaller loan origination and decrease in operating revenue. | Medium- to long-term | Small |
- Accelerate financial services including lowering monthly repay amount to prepare for decreased willingness of consumers to buy houses and shift of demand to pre-owned houses along with increase in new house prices. - Further strengthen relations with pre-owned house providers and consider various measures to establish SBI ARUHI's position as a mortgage bank that strongly supports pre-owned houses. |
|
|
Physical risks |
Acute/ Chronic |
As natural hazards intensify, housing manufacturers may not be able to implement viable disaster management plans. Heat stress may also prevent them from taking viable steps against heat exhaustion. These may cause delay in construction of buildings for which housing loan is to be offered, and lower consumers' willingness to buy houses, leading to smaller housing loan origination and decrease in operating revenue. | Short- to long-term | Medium |
- Consider services to offer disaster-related information to consumers to boost SBI ARUHI's business recognition. - Consider offering additional disaster-resilient services. |
| Acute | As natural disasters intensify, sales branches may be affected and SBI ARUHI may sustain losses from recovery costs and business disruption (reduced operating revenue, occurrance of operating expenses). | Short- to long-term | Medium |
- Define matters associated with business continuity plan and revise as needed. - Implement safety status communication system and improve functionalities. |
|
SBI ARUHI's main product “Flat 35“ housing loans are provided in collaboration with the JHF.
The JHF is reviewing the energy saving technology criteria of new houses for “Flat 35“ in order to accelerate efforts to build a carbon free society. Since April 2023, insulation grade 4 and primary energy consumption grade 4 or higher has been required for all new houses. Technical criteria for energy saving performance may be further strengthened.
With the tightening of energy saving technology criteria by the JHF, there is a risk that more new houses may become ineligible for “Flat 35“.
SBI ARUHI considers actions to build a carbon-free society, including urging the government to implement a policy to promote energy saving initiatives across the housing loan industry, and conducting industry-wide activities to urge the policy to be implemented.
SBI ARUHI also helps mitigate environmental burdens and address climate change by building a stock-based circular society defined in its Materiality (*3). To this end, The Company is committed to building a stock-based circular society by promoting distribution of preowned properties through the homebuying business, and by helping reduce waste through promotion of the second-hand market.
By supporting people to move to pre-owned houses and green their homes and increasing the opportunities to offer housing loans supporting maintainability, manageability, and energy saving performance of houses, SBI ARUHI contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions while expanding profitability.
In the 1.5℃ scenario, housing prices may increase along with the soaring costs of building materials with tightening of regulations on carbon tax, timber, and plastic, and the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings, as well as the implementation of ZEH (net Zero Energy House) requirements. This may drive consumers away from buying houses and cause decrease in housing loan origination.
SBI ARUHI accelerates the launch of new financial products and services such as lowering monthly repayment to prepare for decreased willingness of consumers to purchase houses and shift of demand to pre-owned houses along with the rising new house prices. The Company also strengthens relations with pre-owned house suppliers and aims to establish its position as a mortgage bank that strongly supports pre-owned houses.
In the 4℃ scenario, typhoons around Japan will intensify by 2050, with each typhoon expected to bring more rainfall.(*4) Flood frequency is anticipated to quadruple by 2040.(*5)
As natural hazards intensify, housing manufacturers may not be able to implement viable disaster management plans, leading to delay in construction of houses for which housing loan is to be offered, decreased willingness of consumers to purchase houses, and smaller housing loan origination.
SBI ARUHI considers offering disaster-related information to consumers to boost its business recognition and delivering additional disaster-resilient services.
As natural disasters intensify, sales branches may be affected and SBI ARUHI may sustain losses from business disruption. To provide for these risks, The Company revises matters related to its business continuity plan as needed.
- *3 SBI ARUHI has defined business priorities from the ESG standpoint in Materiality, which is published in its corporate website.(https://www.sbiaruhi-group.jp/english/sustainability/materiality)
- *4 Climate Change in Japan 2020 (full version), Japan Meteorological Agency
- *5 Proposal on flood control plan based on climate change, technical review meeting on flood control plan based on climate change, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, Japan
Climate-related opportunities and key initiatives
Opportunities and key initiatives in scenario analysis
| Category | Major opportunities | Time frame | Financial impact | Key initiatives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Green RMBS, backed by housing loan for energy saving houses, provides strong value to investors. By issuing RMBS under better conditions than conventional RMBS, SBI ARUHI can deliver more benefits with its housing loans to customers who purchase houses with high energy performance, thus boosting operating revenue. | Short- to long-term | Big |
- SBI ARUHI issued the first Green RMBS in Japan, procuring funding for the execution of “ARUHI Super Flat S” housing loans for residential properties that satisfy certain standards on energy saving. - Keep procuring funding from Green RMBS, while aiming to deliver more value and better conditions for investors through further information disclosure. - Support people to move to pre-owned houses and green their homes to increase opportunities to offer housing loans supporting maintainability, manageability, and energy saving performance of houses and drive profitability. |
| Market | As consumer preference transitions to energy saving houses, boost operating revenue by offering preferential loans to customers purchasing houses that help address climate-related challenges. | Short- to long-term | Big |
- Consider implementing measures to encourage consumers to purchase energy saving houses by helping them understand that their choice of a house they buy would address environmental conservation and climate change. - Consider incorporating these viewpoints into product strategy. |
| Reputation | As ESG investments gain momentum, disclosing organizations' climate-related initiatives and non-financial information directly affects their reputation among investors. Disclosure of vigorous climate-related initiatives and non-financial information could attract investment and make SBI ARUHI's stock price go up. | Short- to long-term | Big |
- At its corporate website, SBI ARUHI discloses its initiatives regarding sustainability and climate change. The scope of disclosure will be further expanded. - While closely watching investors' move, SBI ARUHI will procure funding for loans for residential properties that satisfy the technical standards on energy saving by issuing Green RMBS. |
| Policy & legal | Tightening of measures to encourage green renovation for housing stock could spur adoption and demand for high-quality pre-owned houses, leading to preference for housing loans that strongly support pre-owned houses, which may result in more operating revenue. | Medium- to long-term | Medium |
- Consider services helping customers pay for green renovation. - Evaluate the value of properties undergoing renovation, and consider measures to promote pre-owned houses. |
| Reputation | Commitment to offer housing loans that help address climate-related issues directly affects the reputation of a company. By building reputation as a company that vigorously works on these issues, SBI ARUHI can gain competitive advantage over other housing loan providers, thus boosting operating revenue. | Short- to long-term | Medium |
- At its corporate website, SBI ARUHI discloses its initiatives regarding sustainability and climate change. The scope of disclosure will be further expanded. - SBI ARUHI has established the ESG Committee to systematically address climate-related challenges. The company will keep viable, systematic operation. - ARUHI Green Finance Framework has been recognized by the Japan Credit Rating Agency. The company will implement diverse measures to maintain positive ratings. |
Recently, assets under management (AUM) in sustainable investment strategies is increasing rapidly. Sustainable investment balance in Japan (bonds) increased from JPY 146.1 trillion in 2019 to JPY 180.1 trillion in 2020 and JPY 302.9 trillion in 2021.(*6)
As this trend is expected to gain momentum, SBI ARUHI issues Green RMBS that delivers strong value to investors, which allows the company to offer more advantages with its housing loans to customers who purchase energy saving houses. The Company regards this as a great opportunity as this potentially increases housing loan origination in yen value and boosts operating revenue.
As a part of its Materiality initiative to mitigate environmental burden and address climate change by building stock-based circular society, SBI ARUHI procures funds by issuing Green RMBS backed by “ARUHI Super Flat S” housing loan for residential properties that satisfy certain standards on energy saving. The Company continues to procure funding through Green RMBS and offer them with better terms to encourage customers to purchase energy saving houses, thus driving transition to a carbon-free society.
Also as a part of its Materiality initiative, SBI ARUHI helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by promoting pre-owned houses. By supporting people to move to pre-owned houses and green their homes, The Company increases opportunities to offer housing loans supporting maintainability, manageability, and energy saving performance of houses, and drives profitability.
In the market, consumer preference is expected to transition to energy saving houses. SBI ARUHI believes that offering preferential loans to customers purchasing houses that help address climate-related challenges will lead to increasing operating revenue.
SBI ARUHI considers implementing measures to encourage consumers to purchase energy saving houses by demonstrating to them that their choice of a house they buy could help address environmental conservation and climate change.
In the 1.5℃ scenario, investors are likely to be increasingly interested in climate-related challenges and expecting roles that companies play. Disclosing organizations' climate-related initiatives and non-financial information directly affects their reputation among investors. SBI ARUHI believes that actively disclosing information will help improve its corporate value and increase its stock price.
At its corporate website, SBI ARUHI discloses its initiatives regarding sustainability and climate change. The company will further expand disclosure.
- *6 Sustainable Investment Survey in Japan 2021, Japan Sustainable Investment Forum
Risk Management
SBI ARUHI's ESG Task Force collects information about climate-related challenges, conducts research, and identifies and assesses climate-related risks and opportunities that may have financial impact. Risks and opportunities assessed as especially important are discussed at the ESG Committee, which then reports to the Board of Directors.
SBI ARUHI has also established a process to manage climate-related risks and opportunities as described below. The process will be managed and operated adequately to enable a carbon-free society.
The ESG Committee examines and creates a plan for climate-related risks and opportunities identified and assessed as critical business risks and opportunities. CEO, who chairs the ESG Committee, assigns teams that are responsible for taking actions. Assigned teams develop necessary measures and action plans, and carry out the plans. Progress management of these action plans is handled by the Risk Management Office, which oversees risk management across the organization.
The Risk Management Office submits reports on risk management status and risk monitoring results to the ERM Committee consisting of Representative Director and President, Risk Management Officer, and others.
Members of the ESG Task Force include members of the Risk Management Office. Information collected, research results assembled, and risks and opportunities identified and assessed by the ESG Task Force are shared with the Risk Management Office.
Metrics and Targets
In recent years, SBI ARUHI has accelerated sustainability initiatives, including establishing an ESG policy, building an environment for implementation, and expanding disclosure.
The Company's greenhouse gas emissions are measured based on the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) category, which is published on its sustainability web page.
While SBI ARUHI does not emit greenhouse gas associated with production of its products and services, it accelerates initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using renewable energy for its everyday business activities at its head office and sales branches, and by choosing to use facilities that have air conditioning with lower environmental burdens.
SBI ARUHI also sets KPIs to address risks and opportunities identified and assessed in scenario analysis and monitors progress.

